Misconceptions about search engine optimization are common. One of the most common is that once a site is built and submitted to the search engines, heavy traffic is on its way. Another is that when making a submission to each engine, a site will be registered immediately and will stay listed with that engine for as long as it is in operation. That's just not how it works… not even close!
What people need to know is that search engine optimization, which is actually the effective utilization of search engines to draw traffic to a Web site, is an art. It is an ongoing, continuously evolving, high maintenance process that includes the customization of a site for better search engine ranking.
Critical steps to take before submitting
After developing a Web site and selecting the best hosting company, don't rush out and submit it to search engines immediately. A Web site manager would be wise to take a little time to:
Fine tune the TITLE tag to increase traffic to the site
Improving the TITLE tag is one technique that applies to just about all the search engines. The appearance of key words within the page title is one of the biggest factors determining a Web site's score in many engines. It's surprising how many Web sites have simple, unimaginative titles like "Bob's Home Page" that don't utilize keywords at all. In fact, it's not unusual to see entire Web sites that use the same title on every page in the site. Changing page titles to include some of the site's key words can greatly increase the chance that a page will appear with a strong ranking in a query for those key words.
Create gateway pages that are specific to the focus of each site
Key word selection must be done carefully with great forethought and understanding of the search engine's selection criteria for key words. The larger the number of key words that are used, the more the relevance of any one key word is diluted. One way to get around this is to create gateway pages.
Gateway pages are designed specifically for submission to a search engine. They should be tuned with a specific set of key words, boosting the chance that these key words will be given a heavy weight. To do this, several copies of a page should be made, one for each set of key words. These pages will be used as entry points only, to help people find the site, therefore, they don't need to fit within the normal structure of the site. This provides the page developer with greater flexibility in establishing key words and tags that will encourage a stronger ranking with the search engines. Each gateway page then can be submitted separately to the search engines.
Ensuring that site technology won't confuse the search engines
Often the latest technology being built into a site can confuse the search engine spiders. Frames, CGI scripts, image maps and dynamically generated pages are all recently created technology that many spiders don't know how to read. With frames for instance, the syntax of the FRAMESET tag fundamentally changes the structure of an HTML document. This can cause problems for search engines and browsers that don't understand the tag. Some browsers can't find the body of the page and viewing a page through these browsers can create a blank page.
Today only 2% of browsers don't support frames, but many search engine spiders still don't support them. A search engine spider is really just an automated Web browser and like browsers they sometimes lag behind in their support for new HTML tags. This means that many search engines can't spider a site with frames. The spider will index the page, but won't follow the links to the individual frames.
Setting up a NOFRAMES section on the page
Every page that uses frames should include a NOFRAMES section on the page. This tag will not affect the way a page looks but it will help a page get listed with the major search engines. The NOFRAMES tag was invented by Netscape for backward compatibility with browsers that didn't support the FRAME and FRAMESET tags.
Performing a maintenance check
All Web sites should be thoroughly tested using a site maintenance tool in order to catch errors in operation before customers are brought to the site. HTML errors can hinder a search engine spider's ability to index a site, it can also keep a search engine from reading a page or cause it to be viewed in a manner different from how it was intended. In fact, a recent report by Jupiter Communications suggested 46% of users have left a preferred Web site because of a site-related problem. With NetMechanic's
HTML Toolbox or another site maintenance tool, all Webmasters, from the novice to the expert can avoid potential visitor disasters due to site errors.
Finding the best submission service
Selecting a search engine submission service requires careful thought and important decisions. Using an auto submission service is a good place to begin. Most search engines like Alta Vista, HotBot and InfoSeek automatically spider a site, index it and hopefully add it to their search database without any human involvement. Some engines, like Yahoo, are done completely with human review and for many reasons are best submitted individually. Chances are good also, that in the first submission a site will be rejected by several of the engines and will need to be individually resubmitted. There are several online resources for auto submissions. The best ones won't submit a site to Yahoo where the customer is better served doing this on his own.
Understanding the waiting periods
A variety of waiting periods must be endured with each search engine before there is even a hope of being listed. Knowing and understanding these waiting periods before beginning the process can eliminate or at least minimize frustration and confusion. Typical waiting periods for some of the more popular engines are six months with Yahoo; one to two months with Lycos and 4-6 weeks with Excite or is that 4-6months? What they say and what happens in reality can be very different.
Ongoing promotion tasks:
To improve site rankings and increase understanding of the listing process, there are many tasks that can be done on a regular or semi-regular basis. Optimizing rankings within the search engines is also to help ensure that a site attracts the right traffic.
Some of the monthly and weekly promotion tasks are:
Crunching and examining log files
Data contained in log files is an excellent resource for identifying which engines are sending the majority of traffic to a site. It can also show which key words or gateway pages are generating the strongest traffic and what are those visitors doing when they enter the site.
Searching the Search Engines
Conduct a search of the search engines to analyze where the highest rankings of the site have materialized and what keywords are generating the best rankings. Different search engines use different rules to rank pages. Individual gateway pages should be created based on the knowledge and interpretation of what each search engine is using to determine top rankings. Several pages can be tested out on one or more engines and the pages that have the most success can be kept, while the unsuccessful pages can be dumped or revised to achieve a higher ranking.
Learning more about how the search engines work
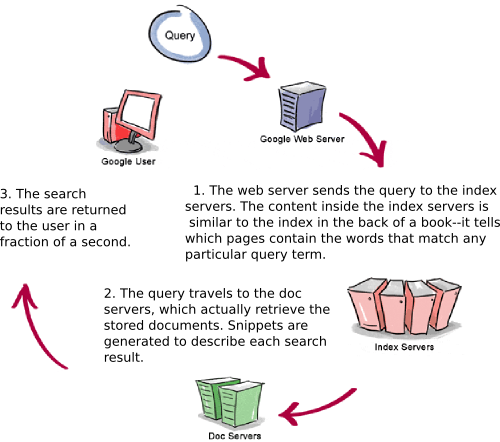
Each search engine uses different rules to determine how well a Web page matches a particular query. As a result, building a single page that gets a good score in all the major engines is just about impossible. Learning how each engine ranks pages is also hard, since the engines often keep this information as a closely guarded secret. However, with a little patience, some experimentation and reverse engineering, the way that many of the search engines work can be discovered.
Resubmitting the site
For engines that reject a site or don't list it high enough, it is strongly recommended that more information is learned about the engine's criteria before resubmitting. This information should then be incorporated into gateway pages or key word revisions in order to have greater success with subsequent submissions. Fine tune the page (or pages) make adjustments to TITLE tags and META tags, then after resubmitting the site, track the results to further learn about the engine's criteria and which adjustments made an impact on the rankings. Don't be afraid to experiment, take some risks and gather data as you proceed.
Checking log files for traffic being directed to erroneous pages on the site
This is good news!! Don't dump these pages or remove them from the search engine as most people will do when they redesign their site. Any page with a high ranking is of value. If a page is bringing traffic to a site, leave that page on the search engine, don't change it but rather redirect the traffic to valid pages in the site.
Getting Noticed
For small to medium-sized Web sites, search engines are the most important source of traffic. Unfortunately, getting noticed in the search engines isn't an easy job. A Web site manager can spend months getting a site listed in an engine, only to find it ranks 50th in their search results. It's hard to give universal tips for improving search engine ranking because each engine has its own set of rules. In general, though, a page will rank well for a particular query if the search terms appear in the TITLE tag, the META tags, and in the body of the page.